Could your virtual wealth be at risk? Is your computer secretly mining cryptocurrency for cybercriminals? Is Your Device a Breeding Ground for Hackers?
Today, I am going to talk about crypto-malware. Here I uncover the hidden dangers of crypto-malware and here you learn how to stay protected. Arm yourself with expert strategies to fend off. Let’s go to begin it.
Introduction
 Crypto malware, also known as ransomware, is a type of malicious software designed to encrypt files on a victim's computer or network, rendering them inaccessible.
Crypto malware, also known as ransomware, is a type of malicious software designed to encrypt files on a victim's computer or network, rendering them inaccessible.
The term "crypto" in crypto malware refers to the encryption process used by the malware to lock the files. Once the files are encrypted, the malware displays a ransom message demanding payment, typically in cryptocurrency such as Bitcoin, in exchange for the decryption key.
In a nutshell, Crypto malware often refers to a type of malware that aims to mine cryptocurrencies on a victim’s computer without detection. It is the unauthorized use of your computer to mine cryptocurrency. This is also known as Crypto-Jacking.
History
 Some highlighted cases that proven the evolution of crypto mining malware and the increasing sophistication of cybercriminals in exploiting vulnerabilities and developing new techniques to generate revenue from illicit mining activities.
Some highlighted cases that proven the evolution of crypto mining malware and the increasing sophistication of cybercriminals in exploiting vulnerabilities and developing new techniques to generate revenue from illicit mining activities.
- TDL-4 (2011): TDL-4 was a rootkit-based botnet that infected millions of computers globally. It was used for various malicious activities, including Bitcoin mining. The botnet was eventually taken down by a joint operation between law enforcement agencies and security companies.
- Mirai (2016): Mirai was a botnet that primarily targeted IoT devices and was initially used for DDoS attacks. However, a variant of Mirai was later discovered that also included crypto mining capabilities, targeting vulnerable IoT devices to mine cryptocurrencies.
- Adylkuzz (2017): Adylkuzz was a crypto-mining malware that exploited the same EternalBlue vulnerability as the infamous WannaCry ransomware. It targeted Windows systems to mine Monero cryptocurrency.
- PyRoMine (2018): PyRoMine was a Monero-mining malware discovered in April 2018. It used the EternalRomance exploit, another tool leaked from the NSA, to propagate and infect Windows systems.
- Skidmap (2019): Skidmap is a Linux-based malware that targeted servers and IoT devices to mine cryptocurrencies. It used various techniques to hide its activities and maintain persistence on infected systems.
Primary Goal
 Taking you to the 5 Years back! In 2018, thousands of government websites in the UK, US, and Australia were found to be running crypto-jacking scripts, affecting visitors to these sites. So, their primary goals have remained the same. Some services stopped whereas some new services have emerged.
Taking you to the 5 Years back! In 2018, thousands of government websites in the UK, US, and Australia were found to be running crypto-jacking scripts, affecting visitors to these sites. So, their primary goals have remained the same. Some services stopped whereas some new services have emerged.
For example, Coinhive was a popular crypto jacking service that allowed website owners to mine Monero cryptocurrency using their visitors' CPU power. It was discontinued in March 2019. Crypto malware has become increasingly prevalent and sophisticated in recent years, posing a significant threat to individuals and organizations alike.
- Unauthorized use of computing resources: Cryptojacking involves secretly using someone else's computer, smartphone, or other devices to mine cryptocurrencies without their permission.
- Generate revenue for attackers: The primary goal of cryptojacking is to generate revenue for the attackers by mining cryptocurrencies using the hijacked devices' processing power.
- Low-risk, high-reward strategy: Cryptojacking is considered a low-risk, high-reward strategy for cybercriminals, as it is often difficult to detect and trace back to the perpetrators.
- Bypass traditional security measures: Cryptojacking can bypass traditional security measures, such as antivirus software, as it doesn't require the installation of malware on the victim's device.
- Exploit vulnerabilities in websites and devices: Attackers often exploit vulnerabilities in websites, software, and devices to inject crypto-jacking scripts, which then run in the background without the user's knowledge.
How Cryptojacking works?
There are two primary ways to get your computer to secretly mine cryptocurrency.
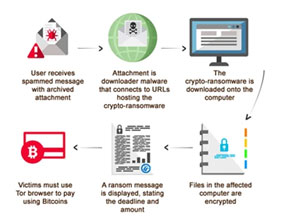 Load crypto mining code on your computer. This is done through phishing. Here, the victim will receive a legitimate email that encourages you to click on a link. The link runs code that places the crypto-mining script on the victim’s device. The script then runs in the background.
Load crypto mining code on your computer. This is done through phishing. Here, the victim will receive a legitimate email that encourages you to click on a link. The link runs code that places the crypto-mining script on the victim’s device. The script then runs in the background.- Inject a script on a website or an ad that is delivered to multiple websites. Once you visit the website where the infected ad pops up in your browser and the script automatically executes.
Symptoms before Crypto-Jacking
 Your device may become noticeably slower
Your device may become noticeably slower- Strains your device's central processing unit (CPU)
- Used extensively for mining activities, increased workload on the CPU and generate more heat
- Your Battery is about to die
Top 8 Crypto Malware/Ransomware in 2023
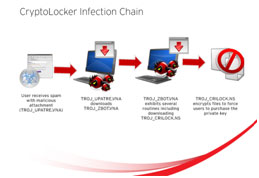 Cryptolocker - CryptoLocker is malware that holds your files for ransom by encrypting them. It is a type of crypto-ransomware. Encryption works by relying on two “keys,” one public key and one private key. Attackers use the public key to encrypt and lock your files. The program will demand a ransom payment to decrypt your files, as only the attackers hold the private key that can decrypt them.
Cryptolocker - CryptoLocker is malware that holds your files for ransom by encrypting them. It is a type of crypto-ransomware. Encryption works by relying on two “keys,” one public key and one private key. Attackers use the public key to encrypt and lock your files. The program will demand a ransom payment to decrypt your files, as only the attackers hold the private key that can decrypt them.- Prometei Botnet - Prometei Botnet aims to install itself on as many devices as possible to mine the Monero cryptocurrency. It is an opportunistic malware (it targets victims randomly) and uses known exploits to spread itself across a network of devices.
- PowerGhost - PowerGhost is a fileless crypto malware that is known to attack corporate servers and workstations, embedding and spreading itself undetected across endpoints and servers. It is capable of disabling antivirus software and other competing cryptocurrency miners to evade detection and obtain the maximum yield of cryptocurrency from an infected device.
 Ryuk - Ryuk is a ransomware strain that targets large organizations for high ransom payouts. It is known for its highly targeted attacks, often using spear-phishing emails and exploiting vulnerabilities in remote desktop services.
Ryuk - Ryuk is a ransomware strain that targets large organizations for high ransom payouts. It is known for its highly targeted attacks, often using spear-phishing emails and exploiting vulnerabilities in remote desktop services.- Conti - Conti is a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) operation that targets corporate networks. It uses a combination of advanced techniques, such as double extortion, where the attackers not only encrypt the victim's data but also threaten to leak it if the ransom is not paid.
- REvil - REvil is another RaaS operation that has been responsible for numerous high-profile attacks. It uses a variety of attack vectors, including phishing emails, software vulnerabilities, and supply chain attacks, to infiltrate and encrypt the victim's data.
- DoppelPaymer - DoppelPaymer is a ransomware strain that emerged from the BitPaymer ransomware family. It is known for its double extortion tactics and has been responsible for attacks on various industries, including healthcare, manufacturing, and government organizations.
- Egregor - Egregor is a ransomware strain that emerged in 2020 and has been responsible for several high-profile attacks. It uses a combination of data encryption and data exfiltration to pressure victims into paying the ransom.
Why Crypto-Jacking is Daily Cup-of-Tea for Hackers?
 Hackers are like black cats. They are ruthless and aim to make money easily. Cryptojacking is the cheapest way and become popular gradually. A more profitable and alternative way for Fraudsters. With ransomware, a hacker might get three people to pay for every hundred computers infected while with crypto-jacking all hundreds of those infected machines work for the hacker to mine cryptocurrency. Crypto mining continuously generates money. The risk of being caught and identified is also much less in this zone. The crypto mining code runs surreptitiously and can go undetected for a long time. Once discovered, it will be hard to get back to the resource.
Hackers are like black cats. They are ruthless and aim to make money easily. Cryptojacking is the cheapest way and become popular gradually. A more profitable and alternative way for Fraudsters. With ransomware, a hacker might get three people to pay for every hundred computers infected while with crypto-jacking all hundreds of those infected machines work for the hacker to mine cryptocurrency. Crypto mining continuously generates money. The risk of being caught and identified is also much less in this zone. The crypto mining code runs surreptitiously and can go undetected for a long time. Once discovered, it will be hard to get back to the resource.
How to stay safe from Crypto Malware?
 Implement Multi-Layered Security just as a fortress has multiple layers of defence
Implement Multi-Layered Security just as a fortress has multiple layers of defence- Keep Software and Systems Up-to-Date
- Enable firewalls
- Implement Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
- Turn on the Data Back-Up system. Include it as a part of your daily habits
- Update password
- Never click on suspicious links or you will fall into the trap of phishing
Conclusion:
Securing your digital assets requires that you take precautions against crypto-malware. You may drastically decrease your chance of becoming a victim of crypto-virus assaults by following these seven safety recommendations. Prioritise cyber hygiene, use caution when downloading and opening email attachments, use MFA, and become knowledgeable about social engineering techniques. You may benefit from cryptocurrencies while reducing your risk of becoming a target for thieves by exercising caution and being proactive. Keep yourself and your digital assets protected.
Similar Blogs:
Hacking Tools
Explore All Hacking Tools »
UFTP is an encrypted multicast file transfer program for secure, reliable & efficient transfer of files. It also helps in data distribution over a satellite link.
Read DetailsBreaking News
Breaking News Of Each Month »
The recent pandemic was unexpected and unknown to most part of the world. It has changed our life and we are slowly adapting to our new lifestyle. The risks associated with the new lifestyle, both personal & corporate, are unknown to most of us.
Read Details