Contents
- Introduction
- What is Ransomware?
- How a Ransomware attack is done?
- How Social Engineering Tactics Fuel Ransomware Attacks?
- Top Industries and Companies Targeted by Ransomware Attacks 2023
- Top 5 Ransomware Family in 2023
- Negotiating with Cybercriminals: Is Paying the Ransom Worth it?
- How Security Awareness Training Can Help Defend Against Social Engineering-Driven Phishing Scams?
- Conclusion
Introduction
RANSOMWARE THREAT "NOT IMMINENT, IT’S UPON US". Ransomware attacks have become a major concern for companies worldwide. With various attacks against things like the colonial pipeline attacks against local governments, school systems, police departments, city halls, and public schools, ransomware is everywhere in the news.
A lot of questions are created like what is ransomware, what types of ransomware exist today, how are new variants of ransomware created, who creates them, is it possible to decrypt files encrypted by ransomware, how to prevent ransomware attacks, and much newer.
These are the questions that need to be on the mind of each person in the world. Ransomware knows no boundaries. These attacks involve hackers infiltrating a company's computer network and encrypting sensitive data, rendering it inaccessible until a ransom is paid. The ransom is usually demanded in the form of cryptocurrency, making it difficult to trace and recover.
Let’s do a complete anatomy of Ransomware from its quick definition. Know your secret enemy.
What is Ransomware?
 Ransomware is a type of malicious software that encrypts a victim's files or data and demands payment in exchange for the decryption key. The goal of ransomware is to extort money from individuals or organizations by threatening to permanently delete or destroy the encrypted data if the ransom is not paid.
Ransomware is a type of malicious software that encrypts a victim's files or data and demands payment in exchange for the decryption key. The goal of ransomware is to extort money from individuals or organizations by threatening to permanently delete or destroy the encrypted data if the ransom is not paid.
Ransomware attacks typically begin with an email or message that contains a malicious attachment or link. Once the attachment or link is opened, the ransomware begins to spread throughout the victim's computer or network, encrypting files as it goes. The victim is then presented with a message that demands payment in exchange for the decryption key.
The ransom demand is typically in the form of cryptocurrency, which makes it difficult to trace the identity of the attacker.
Each operating system has security vulnerabilities. "We are never going to find every bug but the best we can do is as we find bugs, we fix them. But these security vulnerabilities can be exploited."
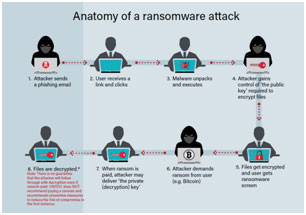
How a Ransomware attack is done?
There are large groups of malicious actors who are constantly scanning, looking at code, searching for these loops, and also keeping eyes to access systems. They are always looking out for a bug, and they will exploit it right then and there to make money.
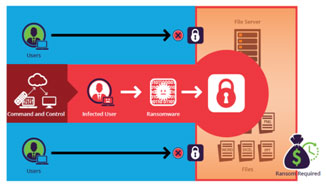
They take the vulnerability in your machine and they are going to transmit some software over the internet into the machine and that software is then going to sit dormant and idle until it gets executed and so it may have a time delay of a day, a week or a month whatever but there will be some sort of a time delay between when the malicious actor accesses the machine and that code is going to encrypt a very large proportion of the files on the machine.  It does not encrypt the core OS. Then it is going to pop something up on the screen like you have been hacked, your system has malware, your device is compromised, and your network has been infected.
It does not encrypt the core OS. Then it is going to pop something up on the screen like you have been hacked, your system has malware, your device is compromised, and your network has been infected.
How Social Engineering Tactics Fuel Ransomware Attacks?
Social engineering tactics are often used as a means to deliver ransomware attacks, which can cause significant harm to individuals and organizations.
- Phishing for Ransom - Phishing for ransom is a common tactic used by cybercriminals to trick victims into falling for their scams and paying a ransom. Social engineering is a key factor in crafting effective phishing emails that trick victims into falling for scams.
- Preying on Trust - Spear phishing attacks are a form of social engineering that targets specific individuals or organizations. Cybercriminals use social engineering tactics to craft convincing emails that appear to come from a trusted source, such as a colleague or a senior executive, or your close ones. By impersonating someone the victim knows and trusts, cybercriminals can manipulate them into clicking on a malicious link or providing sensitive information.
- Spoofing the Spoof-Proof - Business Email Compromise (BEC) is a type of cybercrime that uses social engineering tactics to manipulate individuals into transferring money or sensitive data to cybercriminals. BEC scams often involve the impersonation of high-level executives or authority figures within an organization, creating a false sense of urgency and authority. Cybercriminals use email spoofing, deception, and other social engineering techniques to trick their victims into performing actions that lead to financial loss or data theft.
- Click Here to Encrypt - Social engineering tactics are frequently used to lure unsuspecting victims into clicking on malicious links that can cause significant harm. Cybercriminals use curiosity, deception, fear, urgency, and other social engineering tactics to make their victims believe that the links are legitimate and safe to click. Once clicked, these links can initiate a malware download or redirect the user to a phishing site, leading to data theft or financial loss.
Top Industries and Companies Targeted by Ransomware Attacks 2023
"In 2021, the retail industry experienced the most significant increase in ransomware — 100%. Compared to 2020, the technology sector saw an 89% increase, and healthcare shot up by 30%."
"Some organizations suffered one or more ransomware attacks in 2021. Of that 76%. 42% were unintentionally caused by user actions, such as clicking on malicious links from spam emails."
"43% were due to negligence from managers or administrators (risks concerning software patches, credentials, etc.)"
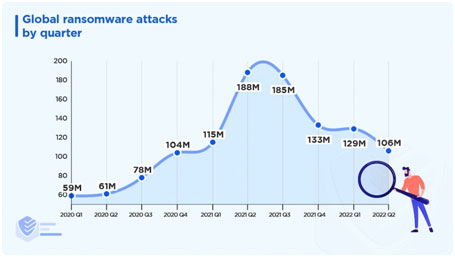
"In the first half of 2022, there were 236.1 million ransomware attempts."
"Some companies choose to pay the ransom, even though it’s generally not recommended and even illegal in some countries."
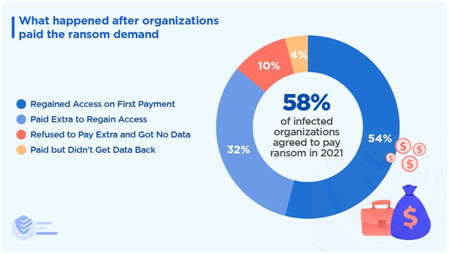
Top 5 Ransomware Family in 2023
1. Lockbit
 Lockbit ransomware is a particularly insidious strain of malware that can leave your computer system held hostage and your important files encrypted until you pay the ransom demand. With its advanced techniques and stealthy infiltration tactics.
Lockbit ransomware is a particularly insidious strain of malware that can leave your computer system held hostage and your important files encrypted until you pay the ransom demand. With its advanced techniques and stealthy infiltration tactics.
This type of ransomware is a force to be reckoned with in the ever-evolving landscape of cybercrime.
"In June 2021, Lockbit released version 2.0 of their RaaS, followed by version 3.0 in June 2022. The latest iteration includes new encryptors based on the BlackMatter source code, as well as new payment methods, extortion strategies, and even a ransomware bug bounty program."
2. Lazarus
 Lazarus ransomware is a notorious threat that has gained notoriety for its ability to wreak havoc on computer systems and cause significant data loss.
Lazarus ransomware is a notorious threat that has gained notoriety for its ability to wreak havoc on computer systems and cause significant data loss.
This malicious software is designed to infiltrate a system, encrypt files, and demand a ransom payment from the victim in exchange for the decryption key.
"The Lazarus Group, a hacker collective with ties to the North Korean government, has had a busy year, with the U.S. government seizing $30 million worth of cryptocurrency stolen by the group in a play-to-earn game scheme in early 2022. Between February and July of that year, Lazarus targeted energy providers in Canada, Japan, and the United States, using vulnerabilities in VMWare Horizon and deploying malware to gain initial access to the organizations."
3. Conti
 Conti ransomware is a formidable adversary in the world of cybercrime. What makes Conti ransomware so dangerous is its ability to spread quickly and evade detection by the security software, making it difficult to contain and neutralize.
Conti ransomware is a formidable adversary in the world of cybercrime. What makes Conti ransomware so dangerous is its ability to spread quickly and evade detection by the security software, making it difficult to contain and neutralize.
Organizations targeted by Conti ransomware must act fast to mitigate the damage and prevent further data loss.
"Conti group targeted the Costa Rican government and launched Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks on Cobalt Strike servers.
The group also targeted the Ukrainian government and various Ukrainian and European humanitarian and non-profit organizations during the Russia-Ukraine conflict. While Conti had previously expressed support for Russia, they later pulled back.
According to Google’s Threat Analysis Group, the group used phishing emails impersonating the National Cyber Police of Ukraine to target their victims."
4. Hive
 The Hive ransomware is known for its ability to remain undetected and spread quickly, causing widespread damage and disrupting business operations.
The Hive ransomware is known for its ability to remain undetected and spread quickly, causing widespread damage and disrupting business operations.
If you fall victim to this malware, you can expect significant financial losses, lost productivity, and potential reputational damage.
"As of November 2022, the FBI has reported that the Hive ransomware group has affected over 1,300 companies worldwide, extorting approximately $100 million in ransom payments. Hive operates using the ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) model, in which developers create, maintain, and update the malware, while affiliates conduct the actual ransomware attacks.
From June 2021 through at least November 2022, Hive has targeted a wide range of businesses and critical infrastructure sectors, including government facilities, communications, critical manufacturing, information technology, and healthcare and public health (HPH) in particular."
5. Black Basta
 Black Basta ransomware is a menacing threat that can cause significant damage to computer systems and hold valuable data hostage. It is difficult to detect and prevent.
Black Basta ransomware is a menacing threat that can cause significant damage to computer systems and hold valuable data hostage. It is difficult to detect and prevent.
"One of the key features of this ransomware is its ability to delete all Volume Shadow Copies and replace them with a new JPG image set as the desktop wallpaper, as well as an ICO file representing the encrypted files.
The files targeted by Black Basta are encrypted using the ChaCha20 algorithm, with the key and nonce being encrypted using a hard-coded RSA public key."
Negotiating with Cybercriminals: Is Paying the Ransom Worth it?
 One wrong move and you could end up in a worse situation than before. But when your company's data is on the line, it's tempting to do whatever it takes to get it back. One option is to pay the ransom. But is it worth it? While it may seem like a quick fix, it can set a dangerous precedent and make you a target for future attacks. On the other hand, refusing to pay may mean losing valuable data forever. It's a delicate balance, but one thing is certain: negotiating with cybercriminals should never be taken lightly. Remember that negotiating with cybercriminals is a tricky business.
One wrong move and you could end up in a worse situation than before. But when your company's data is on the line, it's tempting to do whatever it takes to get it back. One option is to pay the ransom. But is it worth it? While it may seem like a quick fix, it can set a dangerous precedent and make you a target for future attacks. On the other hand, refusing to pay may mean losing valuable data forever. It's a delicate balance, but one thing is certain: negotiating with cybercriminals should never be taken lightly. Remember that negotiating with cybercriminals is a tricky business.
How Security Awareness Training Can Help Defend Against Social Engineering-Driven Phishing Scams?
Human Firewall is enough for raising Awareness to combat social engineering-driven ransomware attacks.
Let’s learn about the Protection Against Ransomware, Best Practices, and Prevention Strategies:
 Good Network Policies including your home network or any commercial network. Configure and set up properly.
Good Network Policies including your home network or any commercial network. Configure and set up properly.- Educating employees on the different types of social engineering tactics that hackers use to trick individuals into divulging sensitive information or performing certain actions.
- Highlighting the signs of phishing scams, such as suspicious emails, unrecognized links, or unusual file attachments, and instructing employees on how to identify them.
- Reinforcing the importance of following established protocols, such as verifying requests for sensitive information or not clicking on links from unknown sources.
- Providing examples of successful phishing attacks and explaining how they could have been prevented.
- Encouraging employees to report suspicious emails or activity to their IT department or security team.
- Conduct regular training sessions and refresher courses to keep employees informed about the latest trends in social engineering and phishing scams.
- Creating a 360° Degree security package within the organization that emphasizes the role of every employee in maintaining the security and integrity of the company's systems and data.
- Conducting simulated phishing attacks to test employees' awareness and response to potential phishing scams and providing feedback on how to improve.
Conclusion
As technology continues to advance, so do the methods and sophistication of cybercriminals. Ransomware attacks have become a pervasive threat, causing millions of dollars in damages and disruptions to businesses and individuals alike.
Today, more than ever, it's crucial for individuals and organizations to take cybersecurity seriously and take proactive measures to protect their digital assets. Beyond today, the future of ransomware attacks remains uncertain. One thing is for sure: the only way to stay ahead of these malicious attacks is to stay informed, stay vigilant, and stay prepared. Prevention is always better than cure when it comes to cybersecurity.
Hacking Tools
Explore All Hacking Tools »
UFTP is an encrypted multicast file transfer program for secure, reliable & efficient transfer of files. It also helps in data distribution over a satellite link.
Read DetailsBreaking News
Breaking News Of Each Month »
The recent pandemic was unexpected and unknown to most part of the world. It has changed our life and we are slowly adapting to our new lifestyle. The risks associated with the new lifestyle, both personal & corporate, are unknown to most of us.
Read Details